The Best Staples for Wood
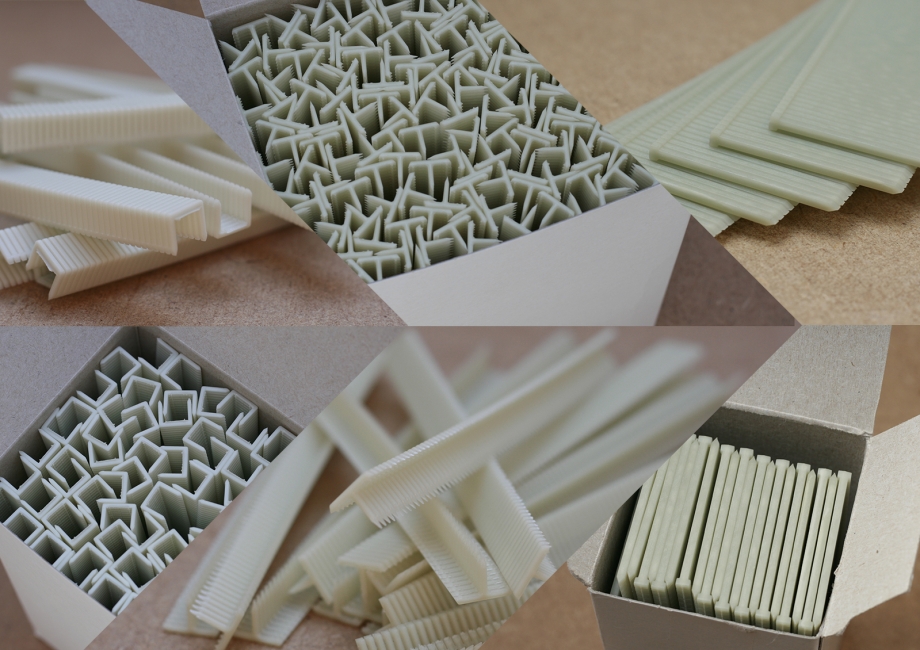
Polymer staples are indispensable wherever corrosion and metal must be avoided. Our staples excel particularly in the wood processing industry.
The advantages of composite staples are evident especially in woodworking.
Wood is marked and then undergoes further processing. During cutting, planing, or milling, it’s crucial to avoid leaving metal staples in the wood, as they can dull and damage milling cutters and saws. Therefore, plastic staples made from a special polymer must be used.
Masterio’s polymer staples do not rust, can be cut and sanded, and do not conduct electricity or magnetize. They can be painted and varnished. They are suitable for woods such as walnut, elm, hazelnut, ash, beech, oak, yew, mahogany, maple, applewood, plywood, Masonite, teak, black locust, hornbeam, red oak, cherry, and pearwood.
Plastic staples have many additional uses, including the production of wood-based panels like MDF, HDF, LDF, or OSB, and laminates. They are also used in yacht manufacturing, wind turbine blades, outdoor advertising, model making, and even coffin production.
U-shaped polymer staples are available in lengths of 7, 10, and 13 mm. We also offer T-shaped polymer brads in lengths of 9 and 12 mm. Additionally, we provide staplers from the Swedish company Titac designed for composite staples and brads.
We also offer composite nails of various lengths and thicknesses, widely used in the USA for roofing, as well as half-inch spaced staples used by some Polish sawmills with staplers from the American company Raptor.
All polymer products are available in soft and hard versions, depending on the type of wood being processed.
If you need plastic (composite, polymer) staples, contact us, and we will help you choose the right product for your needs.